Electrostatic Discharge (ESD), is the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects. This is the same static shock we get when walking across a carpet and then touching a doorknob afterward. This unwanted flow of electricity can disable or severely damage sensitive electronics. As more devices today and in the future get more ESD sensitive, ESD management will be even more crucial.
This article will look at all the things you need to know about ESD management and how you can effectively implement it by utilizing an electronic manufacturing industry consultancy service.
How Does ESD Affect Electronic Devices?
ESD is created by the contact and separation of two materials, most often through direct human contact with other electrically charged objects. Sometimes, the discharge can damage an electric circuit and its components with as little static voltage as 10 volts. This static damage can be categorized into two types: catastrophic and latent failure.
Catastrophic failure is the more visible type of static damage, like melting or explosion, both of which immediately damages a device’s circuitry. This type of failure can be detected when the device is tested prior to shipment. But if the device sustains ESD damage after testing, it might not be detected until the device reaches the consumer’s hands and fails upon operation.
Latent failure, on the other hand, is a less noticeable type of static damage. A device that sustains latent failure may continue to operate normally. Over time, it will sustain subsequent damage resulting in a much reduced operating life, eventually leading to total failure.
How To Prevent ESD
Though ESD can’t be totally eliminated, it can be controlled using these three methods, as recommended by electronic manufacturing industry consultants:
Grounding
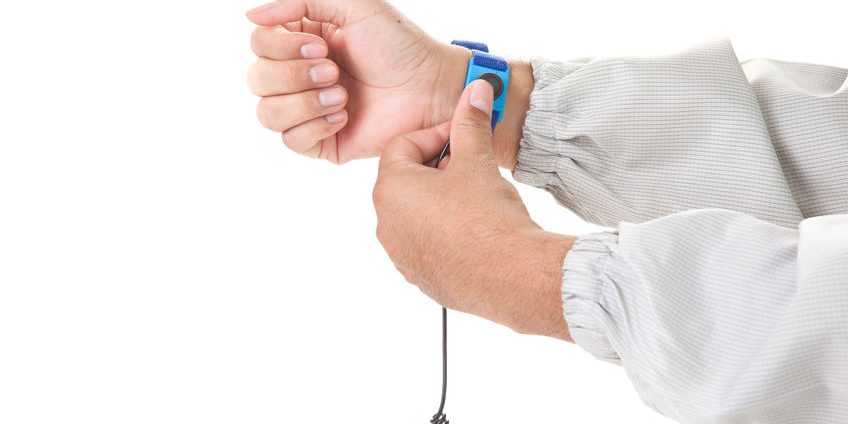
Humans are a primary source of electrostatic energy. You can drain the static charges present on your body before they can potentially be transferred to electronics by using a wrist strap, antistatic clothing, a floor mat, or ESD controlling shoes.
Isolation
The purpose of isolation is to prevent discharge from reaching vulnerable electronics during storage and transportation. This can be done by packing components and assemblies in ESD shielded containers or antistatic packaging made of conductive materials.
Prevention
This method doesn’t require additional materials but instead involves some common sense rules to keep an ESD safe working environment. This includes:
- Testing equipment to check if they are properly grounded
- Opening ESD-sensitive devices at a static-safe workstation
- Keeping the workstation clean and clear of electrostatic generating materials such as plastic cups, Styrofoam packaging, cellphones, sticky notes, or other paper types.
ESD management uses the ESD preventive measures stated above through a comprehensive ESD program consisting of education, best practices demonstrations, signage, and documentations on ESD prevention. The training program, often offered by electronic manufacturing industry consultants, consists of necessary ESD prevention procedures, correct handling of ESD sensitive materials, ESD clothing, and further refresher training for new or updated procedures.
Final Thoughts
ESD can be lethal to sensitive electronics, which is why manufacturing staff must take precautions to prevent it from happening and turning into a costly problem. It is imperative to implement practical ESD prevention protocols as part of ESD management, as it can provide significant returns to the bottom line.
Though establishing and implementing ESD control measures can be a daunting task, there is a way to make that process more manageable. By utilizing an electronic manufacturing industry consultancy service that provides all types of support and guidance to electronics manufacturers.
Contact Blackfox at 888-837-9959 or email Sharon at [email protected] for more information.